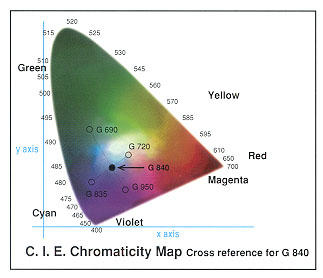
figure above: When you callibrate a monitor, you see this type of color diagram with the white point in the center of a triangular system. This system is based on Thomas Young's tri-stimulous theory. It maps out every color in Nanometers.
Introduction
-Intro
-semiotics
-denotation & connotation
-light & the mechanics of vision
-the basic visual elements
-montage & Mise-en-Scene
Additive Color:
White light is a mixture of colors.
Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727)
Newton's first work as Lucasian Professor was on optics and this was the topic of his first lecture course begun in January 1670. He had reached the conclusion during the two plague years that white light is not a simple entity. Every scientist since Aristotle had believed that white light was a basic single entity, but the chromatic aberration in a telescope lens convinced Newton otherwise. When he passed a thin beam of sunlight through a glass prism Newton noted the spectrum of colours that was formed.
He argued that white light is really a mixture of many different types of rays which are refracted at slightly different angles, and that each different type of ray produces a different spectral colour. Newton was led by this reasoning to the erroneous conclusion that telescopes using refracting lenses would always suffer chromatic aberration. He therefore proposed and constructed a reflecting telescope.
Colorimetry
from link: http://www.cameraguild.com/technology/colorimetry.htm
Light is electromagnetic energy. White light is composed of all colors humans
see, and these colors are measured by their wavelengths in nanometers.

figure above: When you callibrate a monitor, you see this type of color diagram
with the white point in the center of a triangular system. This system is based
on Thomas Young's tri-stimulous theory. It maps out every color in
Nanometers.
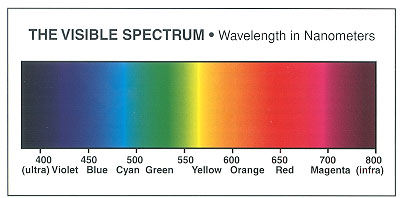
In 1702, Sir Isaac Newton published Optiques. It was the treatise about the physics of color. At that time, scientists knew that putting white light through a prism would divide it into bands of color. But Sir Isaac had the idea to take a second prism and regather the colored light back into "white light." This is how we learned that white light is comprised of all the colors of the rainbow. Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet (hence the acronym, ROY G BIV), Sir Isaac's own description of the color spectrum.
Newton speculated that white light was energy waves of different lengths, and those differences resulted in the color spectrum. Years later, Maxwell and Helmholz were able to accurately measure the wavelengths of light, now known as electromagnetic energy. These wavelengths are measured in nanometers. A nanometer is one billionth of a meter. The red end of the spectrum has long wavelengths from 650-700 nanometers. At the dark blue or violet end of the spectrum are shorter wavelengths from 400 to 450 nanometers.
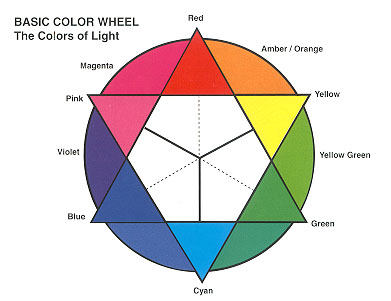
Additive Color Mixing
Sir Thomas Young theorized that three primary colors, red, blue and green, could stimulate the full range of color perception.
Film & Video
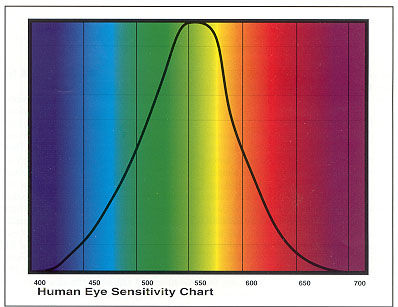
If you compare the average human eye's response to a typical film's response to color, you will see the film designer's attempt to mimic the human eye's perception of color. The main exception is the film's red register, which is deliberately shifted to enhance skin tones. The full color spectrum of (visible light) blue through green, yellow, orange and red is represented in the 400 to 700 nanometer bands.
Energy just below 400 nanometers is ultraviolet, while energy just above 700
nanometers is infrared. Most humans do not "see" energy in the UV
and infrared regions but some film emulsions and video systems do. This is
one reason why cinematographers filming in high altitudes use UV filters to
lower the sky's density, and other unwanted density from Ultra Violet exposure
(or they correct it digitally).
Kelvin Temperature
We measure the color temperature of a theoretical black body radiator in degrees Kelvin. A theoretical black body radiator is a device that radiates no color or light at minus 270°C. As the temperature of the black body radiator rises, it begins to radiate long wave energy. When the temperature reaches about 600° Kelvin (about 870°C) it reaches the threshold of visibility. At 770° Kelvin the black body is dark red. As the temperature rises, the eye can perceive the visible spectrum emitted from the black body as orange, yellow, "white," and finally blue. On the Kelvin temperature comparison chart, sunrise is about 1800° Kelvin. As the sun moves away from the horizon, the ambers and yellows increase and the light takes on the characteristics of an incandescent lamp. Incandescent lamps vary in color temperature from 2600° to 3200° Kelvin. The noonday sun (in Washington, D.C.) has a nominal color temperature of approximately 5400° Kelvin, or "daylight" for film. The amount of blue energy in the spectrum of the noonday sun varies and is dependent upon the region and the weather conditions. If the sky is overcast and cloudy, we will see less blue energy in the spectrum. If the day is clear and bright, the blue sky could be as high as 28,000° Kelvin and the resulting blue energy is greater.
Degrees Kelvin is an important tool for measuring the light sources used in theatre, television, and film production.
Albert Einstein (1879-1955)
The speed of light is constant. The speed of light is constant, but only when it's traveling somewhere where there's nothing to get in its way--like some really empty part of space. There light would travel about 300,000 km per second.
How Fast Is That?
How fast is 300,000 km per second? Really fast? Nothing we know of travels
faster than the speed of light.
If you were traveling at the speed of light it would take about. . .
* eight minutes to travel from the Sun to the Earth.
* one second to circle the Earth seven times.
Some things can slow down light, such as glass, crystals, or diamonds.